The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care
The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care
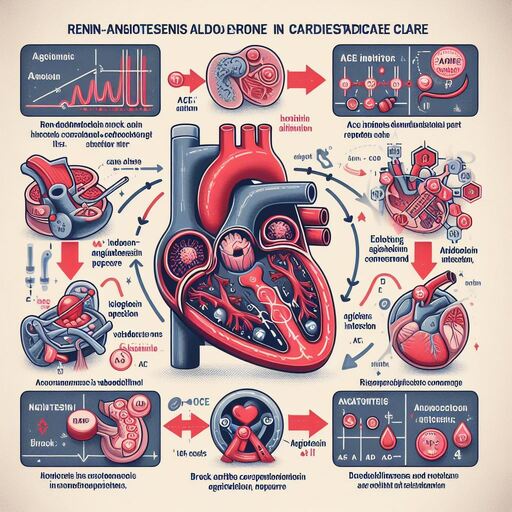
In the realm of cardiovascular medicine, ACE inhibitors (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors) have emerged as a cornerstone of treatment for various cardiovascular conditions, offering profound benefits in improving heart health and overall well-being. Let’s delve into the mechanism of action, therapeutic uses, benefits, and considerations surrounding ACE inhibitors in cardiovascular care.
The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care
Understanding ACE Inhibitors
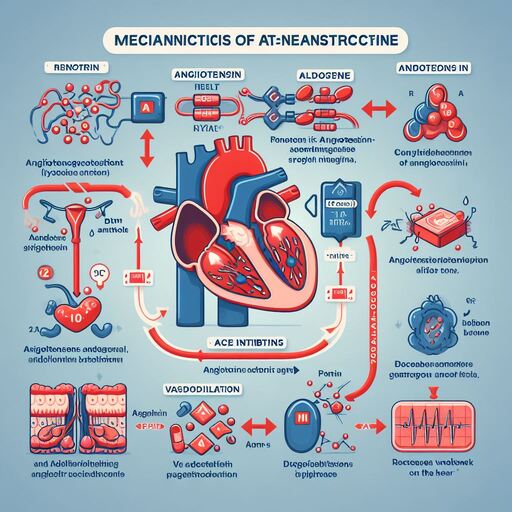
ACE inhibitors are medications that work by blocking the action of the enzyme Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) in the body. This enzyme plays a crucial role in the regulation of blood pressure by converting angiotensin I into angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that narrows blood vessels and raises blood pressure. By inhibiting ACE, these medications cause blood vessels to dilate (widen), leading to decreased blood pressure and improved blood flow to the heart and other organs.
The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care
Therapeutic Uses
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): ACE inhibitors are widely prescribed as first-line agents for the treatment of hypertension. By reducing blood pressure, these medications help lower the risk of complications associated with high blood pressure, such as heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage.
- Heart Failure: ACE inhibitors are an essential component of treatment for heart failure, a condition characterized by the heart’s inability to pump blood effectively. These medications help dilate blood vessels, reduce strain on the heart, and improve cardiac output, thereby alleviating symptoms and slowing disease progression.
- Post-Heart Attack Management: ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed to individuals who have had a heart attack (myocardial infarction) to improve heart function and reduce the risk of future cardiovascular events.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: In certain cases of chronic kidney disease, particularly those associated with diabetes, ACE inhibitors can help slow the progression of kidney damage by lowering blood pressure and reducing stress on the kidneys.
Benefits of ACE Inhibitors
- Blood Pressure Control: ACE inhibitors effectively lower blood pressure, making them valuable in the management of hypertension. Controlled blood pressure reduces the risk of cardiovascular events and organ damage.
- Cardiovascular Protection: Beyond blood pressure control, ACE inhibitors offer cardiovascular protection by reducing the workload on the heart and improving blood flow to the coronary arteries. This can help prevent complications like heart attacks and strokes.
- Heart Failure Management: ACE inhibitors improve symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue, by enhancing cardiac function and reducing fluid buildup in the lungs.
- Renoprotective Effects: In individuals with chronic kidney disease, ACE inhibitors can slow the progression of kidney damage and reduce proteinuria (excess protein in urine), ultimately preserving kidney function.
Considerations and Potential Side Effects
While ACE inhibitors are generally well-tolerated, they may cause certain side effects, including:
The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care
- Dry Cough: A persistent dry cough is a common side effect of ACE inhibitors, affecting some individuals. This side effect may necessitate switching to an alternative medication class.
- Hyperkalemia: ACE inhibitors can increase blood potassium levels, particularly in patients with underlying kidney disease or those taking potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics.
- Angioedema: Rarely, ACE inhibitors can cause swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema), which can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
- Kidney Dysfunction: In rare cases, ACE inhibitors can worsen kidney function, especially in patients with severe renal impairment.
Patient Education and Monitoring
The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care
Patients prescribed ACE inhibitors should be educated about the importance of adherence to treatment, regular blood pressure monitoring, and reporting of any concerning symptoms to their healthcare provider. Routine blood tests to monitor kidney function and electrolyte levels may be recommended, especially in high-risk individuals.
Conclusion
ACE inhibitors represent a powerful therapeutic tool in cardiovascular care, offering significant benefits in managing hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions. By improving blood pressure control, reducing cardiovascular risk, and preserving organ function, these medications play a pivotal role in enhancing heart health and overall quality of life for millions of individuals worldwide. However, like all medications, ACE inhibitors should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, with close monitoring for potential side effects and therapeutic response. With ongoing research and advancements in cardiovascular medicine, ACE inhibitors continue to unlock new possibilities in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.
The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care
The Power of ACE Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Care