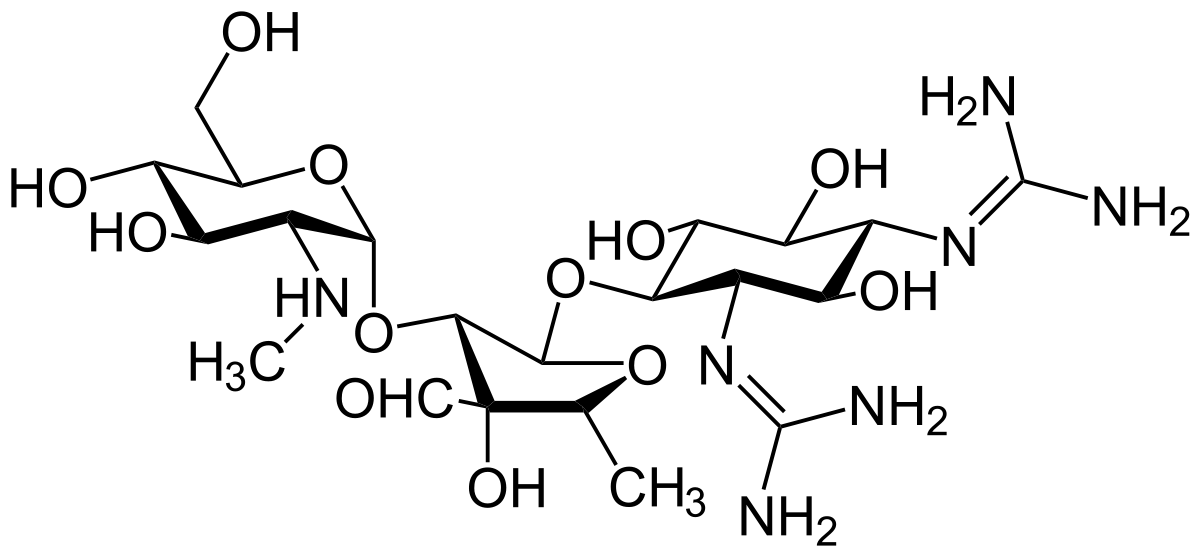
Aminoglycosides are a type of antibiotic that target the ribosomes in bacterial cells, inhibiting the production of proteins necessary for cell growth and survival. They are commonly used to treat bacterial infections in a variety of settings, including respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections.
Aminoglycosides work by binding to the ribosomes in bacteria, causing the formation of a complex that disrupts the normal function of the ribosome. This leads to the inhibition of protein synthesis, which is essential for bacterial growth and reproduction.
The most commonly used aminoglycosides include gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin. These drugs are typically administered intravenously or topically to target bacterial infections in various parts of the body.
Aminoglycosides can have some side effects, including hearing loss and kidney damage. However, these side effects are usually reversible with appropriate management, and the benefits of using aminoglycosides to treat bacterial infections typically outweigh the risks.
It’s important for individuals taking aminoglycosides to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions closely and report any symptoms or side effects promptly. Additionally, it’s important to complete the full course of treatment prescribed by a healthcare provider, as incomplete treatment can lead to bacterial resistance and make future infections more difficult to treat.