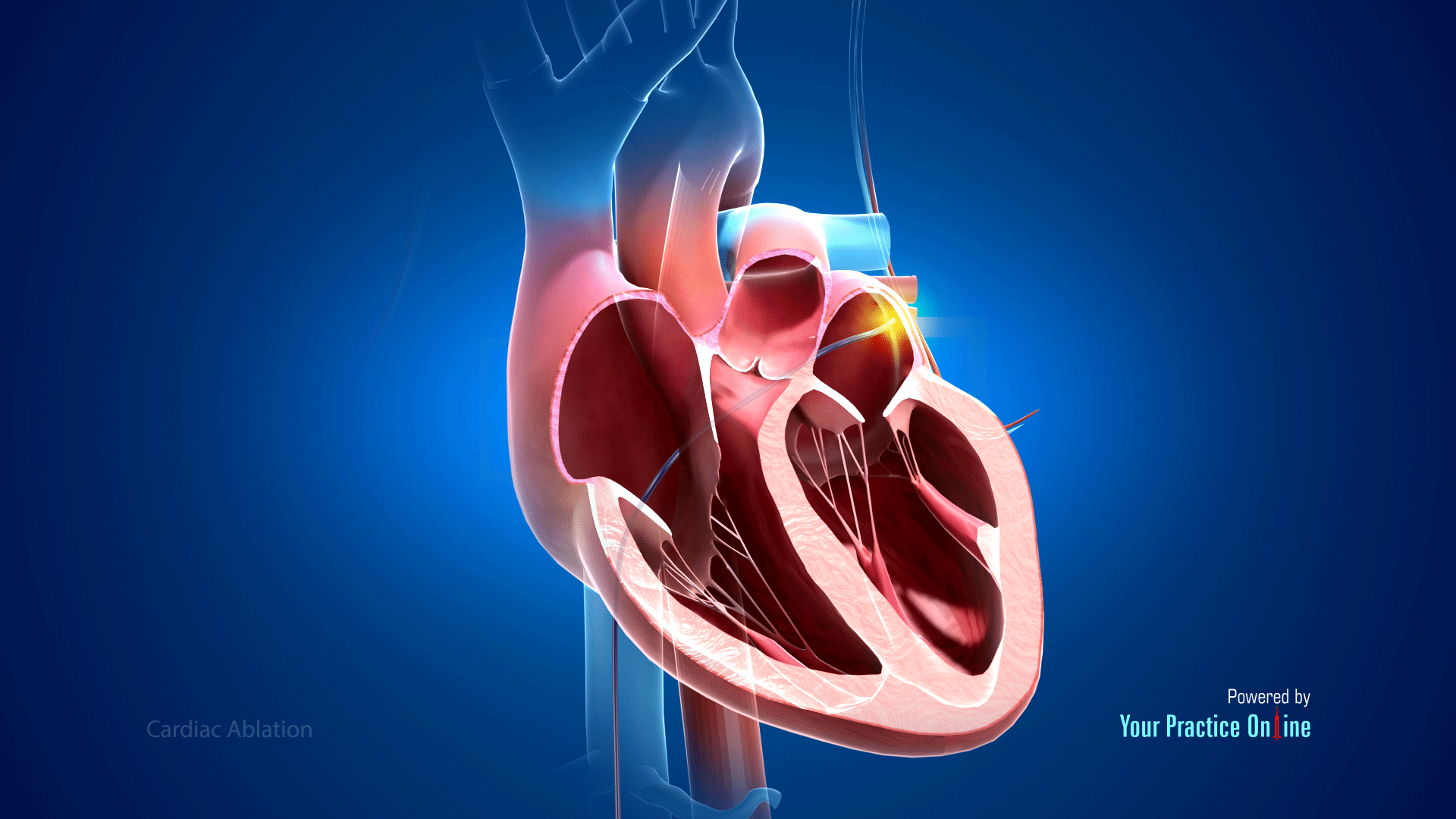
Ablation is a medical procedure that involves the removal of tissue or other structures from the body. It can be performed through various methods, such as surgery, radiation therapy, or cryotherapy.
Ablation may be used to treat a variety of conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and arthritis. For example, radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to heat and destroy tissue in the liver, thymus gland, or other organs. Cryoablation involves freezing the targeted tissue to destroy it, while laser ablation uses high-intensity light beams to vaporize or cut away the affected tissue.
Ablation procedures are typically performed on an outpatient basis and require local anesthesia or general anesthesia. The procedure itself usually takes only a few minutes, and patients can recover quickly with minimal discomfort.
While ablation procedures have a low risk of complications, as with any medical procedure, there is always some level of risk involved. Patients should discuss the benefits and risks of ablation with their healthcare provider before deciding whether it’s the right treatment option for them.